Table of contents of the page
En Ok Pool Reform within Swimming pool water treatment We will give you all the details about the Formula and effects of sodium hypochlorite: chlorine gas in swimming pool water treatment within the section of the page Secrets of pool chlorine disinfection.
What is sodium hypochlorite

What is chlorine GAS?
Chlorine gas definition
In the first instance, it should be mentioned that Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl) is a compound that is used on a large scale for surface purification, whitening, odor elimination and water disinfection.
What is the trade name of sodium hypochlorite?
sodium hypochlorite synonyms
On the other hand, specify that Sodium hypochlorite is known as: bleach, bleach, limpid, bleach, sodium hypochlorite, Giweissi Water, Jane Clarasol Water (very common)
What is the difference between chlorine and sodium hypochlorite?

Chlorine is the common name for sodium hypochlorite solution
In this way, sodium hypochlorite is diluted in water, normally marketed in different concentrations and used as a cleaning, disinfectant, bleaching and stain removing agent.
What is the difference between chlorine and bleach?


Sodium hypochlorite gas vs bleach
At the same time, the main difference between bleach and chlorine is that the former is a product whose active chlorine content is not less than 35 grams per liter nor more than 60 grams per liter.
Bleaching liquids are not the same as chlorine
An important product manufactured from chlorine is bleaching liquid, which people sometimes confuse with chlorine. Bleaching liquid contains a compound called sodium hypochlorite. If you mix an acidic substance with bleaching liquid, chlorine gas can form.
What does chlorine gas mean?
Chlorine gas is produced industrially from sodium chloride.
In the laboratory, controlled, when a small amount of gas is needed, it can be obtained by the reaction of manganese dioxide or hydrochloric acid, which can also be equated: MnO2 (s) + HCL (aq) -> MnCL2 (aq) + H2O (I) + CL2 (g) With this reaction you want to use 29 g of manganese dioxide
What is chlorine gas

gas mixed with chlorine
| Chlorine is a gas with a highly irritating odor. | It is very unstable and reacts quickly with many substances to form other chemicals. |
|---|---|
| Chlorinated water does not contain chlorine gas | Many people mistakenly believe that chlorinated water contains molecular chlorine (Cl2 ). At the beginning of the water chlorination process, molecular chlorine gas can be added to the water; However, it is quickly transformed into other chemical substances, which are what disinfect the water. Hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite anion are two such substances that disinfect water. The term “free chlorine” in drinking water generally refers to the amount of hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite in the water. It is important to know that these substances are different from molecular chlorine. |
History of chlorine gas
Who discovered sodium hypochlorite?

Chlorine gas discovered in 1774
Sodium hypochlorite was discovered in 1774 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele, and eleven years later the Frenchman Claude Berthollet demonstrated its properties.
who invented sodium hypochlorite

Who created chlorine gas cl2
In 1789, the French chemist Claude Louis Berthollet (1748-1822) synthesized a new compound with disinfectant and bleaching properties that he called Javel water. It was sodium hypochlorite, which is also commonly known as bleach.
When did chlorine gas come into use?
Sodium hypochlorite began to be used in the textile industry, to bleach cotton fabrics, and at the end of the XNUMXth century
But, at the end of the XNUMXth century, it was a time when Louis Pasteur discovered that microorganisms are the cause of infectious diseases, achieving its popularization as an antiseptic.
Thus, bleach powder, a combination of chlorine and milk of lime, was the main bleaching agent until the 1920s. Only then was it replaced by liquefied chlorine and sodium hypochlorite.
Sodium hypochlorite uses today

Sodium hypochlorite uses in the present
Sodium hypochlorite is used today in water treatment, in bleaching textiles and in the manufacture of cleaning products. Domestic hygiene and disinfection remain its main daily uses.
physical chlorine gas

Chlorine gas what is it for?
How chlorine gas works
El chlorine gas It is a greenish-yellow, poisonous and oxidizing substance, which is used to oxidize the heavy metals contained in water, eliminate bacteria and guarantee optimal quality for consumption.
Chlorine gas application
El chlorine has applications very varied in the chemical industry, e.g. e.g. in the manufacture of chlorinated organic products (plastic or synthetic material, solvents, insecticides, herbicides), in the pulp and paper industry and in laundries as a bleaching agent.
What is chlorine gas and its effects

Chlorine gas and its effects
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) identifies the most serious hazardous waste sites in the nation. EPA then places these sites on the National Priorities Listexternal icon (NPL) and designates them for long-term cleanup by the federal government. Chlorine gas is too reactive to be detected at hazardous waste sites. Any amount of chlorine gas discharged at these sites will be rapidly transformed into other substances whose original sources may not necessarily have been chlorine.
When a substance is released from a large area, for example from an industrial plant, or from a container such as a barrel or bottle, the substance enters the environment. This release does not always lead to exposure. You can be exposed to a substance only when you come into contact with it? by breathing in, eating or drinking the substance, or by contact with your skin. Because chlorine is very reactive, it is unlikely that you will be directly exposed to this substance unless a large amount is accidentally released nearby.
There are many factors that determine whether exposure to chlorine will harm you. These factors include the dose (how much), duration (for how long), and how you came into contact with this substance. You should also consider the other chemicals you are exposed to, your age, sex, diet, personal characteristics, lifestyle, and health condition.
How much chlorine gas is obtained when treating 80g
How much chlorine gas
Based on the chemical reaction provided, the corresponding conversion factors are proposed to calculate the amount of chlorine gas Cl2(g) obtained by treating 80 g MnO2 with excess HCl as follows:
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
87g 71g
80 g MnO2 * 71 gCl2 / 87 g MnO2= 65.28 g Cl2.
Chlorine gas properties

Sodium hypochlorite technical sheet
| Chlorine gas characteristics | Sodium hypochlorite technical sheet |
|---|---|
| Tradename | Chlorine Liquefied Gas |
| Chemical name | Chlorine Gas |
| Chlorine gas symbol | Cl |
| Chlorine gas Chemical Formula | Cl2 |
| Chlorine gas belongs to the family of: | Chlorine is one of four closely related chemical elements that have been called halogens. |
| Who discovered sodium hypochlorite | Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1774 |
| Who invented sodium hypochlorite? | Claude Louis Berthollet in 1789. |
| Presence on earth: | It is estimated that 0.045% of the Earth's crust is chlorine, since it is the second in reactivity among the halogens, only after fluorine, and hence it is found free in nature only at the high temperatures of volcanic gases. |
| How chlorine gas exists | To begin with, chlorine exists as a yellow-green gas at ordinary temperatures and pressures. |
| How chlorine gas is formed | Chlorine present in nature is formed from stable isotopes of mass 35 and 37; Radioactive isotopes have been artificially prepared. |
| Combination of chlorine gas with other elements | Fluorine is the most chemically active; iodine and bromine are less active. Chlorine replaces iodine and bromine in their salts. It intervenes in substitution or addition reactions with both organic and inorganic materials. Dry chlorine is somewhat inert, but wet it combines directly with most elements. |
| Atomic number | 17 |
| Valencia | +1, -1,3,5,7 |
| Oxidation state | -1 |
| Electronegativity | 3.0 |
| Covalent radius (Å) | 0,99 |
| Ionic Radius (Å) | 1,81 |
| Atomic radius (Å) | - |
| Electronic configuration | [Ne]3s23p5 |
| First ionization potential (eV) | 13,01 |
| Chlorine gas atoms / Atomic mass (g / mol) | 35,453 |
| Chlorine gas molecular weight; | Diatomic gas has a molecular weight of 70.906. |
| Chlorine gas density (g/ml) | 1,56 |
| Boiling point (ºC) | The boiling point of liquid chlorine (golden-yellow in color) is –34.7ºC at 760 mm Hg (101.325 kilopascals). |
| Thermodynamic properties of chlorine gas | Thermodynamic properties include the heat of sublimation, which is 7370 (+-) 10 cal/mol a OK; the heat of vaporization, 4878 (+-) 4 cal/mol; at –34.05ºC; the heat of fusion, 1531 cal/mol; the heat capacity, 7.99 cal/mol at 1 atm (101.325 kilopascals) and 0ºC, and 8.2 at 100ºC. |
| Melting point (ºC) | And the melting point of solid chlorine is –100.98ºC. |
| Tempercritical temperature chlorine gas | 144ºC |
| Critical pressure | 76.1 atm (7.71 megapascals) |
| Critical volume | 1.745 ml / g |
| Chlorine gas critical density | 0.573 g / ml |
Chlorine gas is a simple or compound substance

It combines with metals, non-metals, and organic materials to form hundreds of compounds.
Other sources of chlorine emission have their origin in:
- The production of paper where it is used in the bleaching of the pulp, although currently it tends to be replaced by chlorine dioxide, (ClO2).
- The production of vinyl chloride, an organic compound that is mainly used in the synthesis of polyvinyl chloride, also known as PVC.
- The synthesis of numerous organic and inorganic compounds, for example carbon tetrachloride, CCl4, or chloroform, CHCl3, and different metal halides.
- The preparation of pure hydrogen chloride; carried out by direct synthesis, according to the reaction: H2 + Cl2 —- 2HCl.
Sodium hypochlorite safety sheet insht

What are the international Chemical Safety Cards (FISQ)
The International Chemical Safety Cards (FISQ), the Spanish version of the International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs), collect essential health and safety information on chemical substances verified by an international working group. The ICSCs are a joint production between the International Program on Chemical Safety (IPCS), in which the World Health Organization and the International Labor Office participate, the European Commission and a global network of participating institutions, including the INSST.
Sodium hypochlorite safety sheet
Subsequently, we leave you the link so that you can access the official link of the sodium hypochlorite safety sheet insht.
Chlorine gas uses

Chlorine gas for water treatment

Sodium hypochlorite water treatment
Another of its common uses is in the treatment of water for human consumption, once its turbidity has been eliminated.
Generally, the concentration of sodium hypochlorite for water purification cannot exceed 10%, and the amount of the product must be between 0.5 and 1 mg/l.
It should be noted that the sodium hypochlorite used in this procedure is not commercial chlorine, since the latter contains other chemicals that can be harmful to human health.
Additionally, it is worth mentioning that it is also used to treat wastewater and industrial water. This is because it eliminates unpleasant odors and prevents the spread of bacteria and sludge.
Likewise, it is an ideal component in the treatment of swimming pool water where it is used in a concentration of approximately 12,5% of active chlorine, thanks to its oxidation capacity. Thus, the spread of diseases that can spread in water is prevented and the microorganisms present in it are eliminated.
Chlorine gas as a pool disinfectant

Sodium hypochlorite for swimming pools
Likewise, it is an ideal component in the treatment of swimming pool water where it is used in a concentration of approximately 12,5% of active chlorine, thanks to its oxidation capacity. Thus, the spread of diseases that can spread in water is prevented and the microorganisms present in it are eliminated.
Sodium hypochlorite dental use

Sodium hypochlorite dental use
Sodium hypochlorite is also used in solutions as an irrigation agent in some dental procedures as it helps combat bacterial infection, spores, fungi and the spread of viruses. Additionally, it helps dissolve dead tissue.
Solutions for this type of use have a very low concentration of sodium hypochlorite and are widely used given their effectiveness and low price.
It should be noted that this compound—in minimal concentrations—is also used in the health field to treat eczema.
Sodium hypochlorite medicinal use
Chlorine gas medicinal use
Likewise, it is a very useful product in the disinfection of surgical material or tools that require a high level of sterilization.
Sodium hypochlorite uses in industry

Chlorine gas to bleach fabrics and fabrics
Another common use of bleach or sodium hypochlorite is to bleach fabrics. This is done with the goal of achieving a worn or aged look quickly. This process is generally carried out on linen, denim and cotton garments.
Chlorine gas risks application explosion

chlorine gas how to use
| DANGERS | PREVENTION | FIGHT AGAINST FIRE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIRE AND EXPLOSION | Not combustible but facilitates the combustion of other substances. Many reactions can cause fire or explosion. Fire and explosion risk. See Chemical Hazards. | DO NOT put in contact with combustible substances. Closed system, ventilation, explosion-proof electrical and lighting equipment. Do not expose to friction or shock. | In case of fire in the environment: use a suitable extinguishing medium. In case of fire: keep drums and other installations cold by spraying with water. Fight the fire from a protected place |
Effects of Chlorine on health

Where does chlorine exposure occur?
Chlorine exposure can occur in the workplace or in the environment from releases into the air, water, or soil.
People who use bleach in their laundry and chemicals containing chlorine are not usually exposed to chlorine itself. Chlorine is generally only found in industrial facilities.
Chlorine enters the body when contaminated air is breathed or consumed with contaminated food or water. It does not remain in the body, due to its reactivity.
The effects of chlorine on human health depend on the amount of chlorine present, and the time and frequency of exposure. The effects also depend on the health of the person and the conditions of the environment when the exposure took place.
Recommendations about sodium hypochlorite

What recommendations has the federal government made to protect public health?
The federal government develops regulations and recommendations to protect public health.
Regulations can be enforced by law. The EPA, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are some federal agencies that develop regulations for toxic substances. The recommendations provide valuable guidance to protect public health, but cannot be imposed by law. The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) and the CDC's National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) are two federal agencies that develop recommendations for toxic substances.
Regulations and recommendations may be expressed as “levels-not-to-exceed”, in other words, levels of the toxic substance in the air, water, soil or food that do not exceed critical levels which are generally based on levels that affect animals. These levels are then adjusted for the protection of humans. These “levels-not-to-exceed” sometimes differ among federal organizations due to different durations of exposure (an 8-hour day or a 24-hour day), the use of different animal studies, or other factors.
Recommendations and regulations are periodically updated as additional information becomes available. For the most recent information, consult the issuing organization or federal agency.
The following are some regulations and recommendations for chlorine:
| EPA Air Levels | The EPA has set a limit for chlorine in air at 0.5 ppm. Exposure to higher levels may cause discomfort and irritation. Depending on the concentration, these effects may be reversible when exposure ceases. |
|---|---|
| OSHA Occupational Air Levels | OSHA has set a legal limit of 1 ppm for chlorine in air. This level must not be exceeded at any time. |
| Levels in drinking water established by the EPA | The EPA has established a maximum contaminant level (MCL) and a maximum residual disinfection level (MRDL) of 0.4 mg/L for free chlorine in drinking water. |
How can families reduce the risk of chlorine exposure?

Reduce danger of exposure to chlorine
| Do not mix bleach with other cleaning liquids | When bleach is mixed with other cleaning liquids that contain an acid, such as toilet cleaners, chlorine gas may be released. Mixing bleach with ammonia also produces toxic gases, such as chloramines. |
|---|---|
| Store household chemicals out of the reach of children | To prevent accidental poisoning, always store household chemicals in their original labeled containers and out of the reach of children. Never store these products in containers attractive to children, such as soda bottles. |
| Follow the instructions to disinfect pool water | Chlorine gas can also be released when pool water disinfection products are used improperly. If you have a pool at home, read the label on chlorination products carefully and do not allow children to play with these products. |
Is there any medical test that shows that I have been exposed to chlorine?
Coexisting tests for the manifestation of contact with chlorine
| There are no medical tests for chlorine | There is no medical test to determine if you have been specifically exposed to chlorine. In the body, chlorine is transformed into chloride, a natural component of the body. To detect a significant increase in chloride in the blood, a person would have to ingest or inhale a huge amount of chlorine. This has occurred in a few cases of ingestion of very large amounts of hypochlorite solutions; one of these cases was a fatal case. |
|---|
Risk level of chlorine gas
1st effect sodium hypochlorite
Chlorine gas poisons
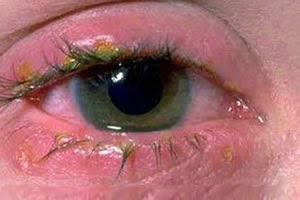
Chlorine poisoning
Poisoning with chlorine can cause symptoms in many parts of the body: causes or may cause difficulty breathing (inhalation), inflammation of the throat, pulmonary edema, sore throat, pain or burning in the nose, eyes, ears, lips or tongue, burns in the tube digestive, abdominal pain, vomiting
Eye contact: Liquid or gaseous chlorine
In high concentrations it causes blurred and distorted vision, redness, pain and severe burning of the ocular tissue, causing blindness.
Chronic exposure: Low concentration of chlorine gas in the air produces light
irritating symptoms after hours of exposure.
2nd sodium hypochlorite effect
Chlorine gas information: reactive product
Chlorine is a highly reactive gas.
It is an element that occurs naturally. The largest consumers of chlorine are companies that produce ethylene dichloride and other chlorinated solvents, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resins, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and propylene oxide. Paper companies use chlorine to bleach paper. Water and wastewater treatment plants use chlorine to reduce the levels of microorganisms that can spread diseases among humans (disinfection).
3st effect sodium hypochlorite
Chlorine gas inhalation

Chlorine gas inhalation
:Chlorine gas is extremely irritating to the mucous membrane of the respiratory system, producing nausea, headaches and blocking the nervous system.
At high concentrations, breathing difficulty increases to the point of death from suffocation or chemical pneumonia.
Breathing small amounts of chlorine for short periods of time negatively affects the human respiratory system.
The effects range from cough and chest pain to water retention in the lungs. Chlorine irritates the skin, eyes and respiratory system.
These effects are not likely to occur at chlorine levels normally found in nature.
The human health effects associated with breathing or consuming small amounts of chlorine over prolonged periods of time are not known.
Some studies show that workers develop adverse effects when exposed to repeated inhalations of chlorine, but others do not.
4nd sodium hypochlorite effect
Chlorine gas irritation on skin contact

Chlorine gas causes local irritations and burns.
5nd sodium hypochlorite effect
Ingestion of liquid chlorine is not possible

Chlorine gas vaporizes gas, as its name indicates, so it is not possible to ingest it. Skin contact:
How can chlorine exposure occur?

| Most people will not be exposed to chlorine | Because chlorine is very reactive, it is generally not detected in the environment except at very low levels in marine air. |
|---|---|
| Accidental exposure to chlorine | If there is an accident, such as a liquid chlorine spill, a chlorine leak from a tank, or a plant that manufactures or uses chlorine, you can be exposed to chlorine by breathing contaminated air or by skin or eye contact with chlorine. .You can also be exposed to chlorine if you mix household chemicals, such as bleaching liquid and toilet flushing liquid.Hypochlorous acid is used to treat swimming pool water. You can be exposed to chlorine gas if you use these chemicals improperly. |
| The air in the workplace | People who work in places where chlorine is used or manufactured may be exposed to low levels of chlorine during their time on the job. Exposure to high levels may occur during the accidental discharge of large amounts of chlorine. |
How does chlorine enter and leave the body?

| Chlorine gas enters your body only when you breathe it | Chlorine gas can enter your body through your nose or mouth. At low concentrations (less than 10 ppm), almost all of the chlorine is removed from the air in the upper respiratory tract and only a very small amount can reach the lungs. lungs.If you drink a hypochlorite solution, it can react with the acid in the stomach and form chlorine gas. |
|---|---|
| Reacts immediately with other chemicals | Chlorine gas reacts with water in cells located on the surface of the airways and forms other compounds that cause irritation. Most of these compounds are eventually transformed into chloride, a normal component of the body. |
How can chlorine affect my health?
This section presents information about possible health effects on humans and animals.
| Brief exposure to chlorine gas | The following effects have been observed in humans briefly exposed to chlorine: mild nose irritation at 1–3 ppm eye irritation at 5 ppm throat irritation at 5–15 ppm immediate chest pain, vomiting, respiratory rhythm disturbances, and cough at 30 ppmlung damage (toxic pneumonia) and pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) at 40–60 ppmdeath after 30 minutes of exposure at 430 ppmdeath after a few minutes of exposure at 1,000 ppmThese concentrations are approximate; The effects also depend on the duration of exposure. In general, people who suffer from conditions such as allergies or hay fever, or those who smoke a lot, tend to suffer more serious effects than people in good health or people who do not smoke. |
|---|---|
| Prolonged exposure to chlorine gas | No harmful effects have been described in workers exposed for years to relatively low concentrations of chlorine (about 1 ppm). In animals exposed for a long time, effects were mainly observed in the tissues inside the nose. |
| Brief oral exposure by ingestion of hypochlorite solution | Drinking small amounts of a hypochlorite solution (less than a cup) can cause irritation of the esophagus. Drinking a concentrated hypochlorite solution can seriously damage the upper part of the digestive tract and may cause death. These effects are probably caused by the corrosive properties of the hypochlorite solution and not by exposure to molecular chlorine. |
| Prolonged oral exposure through ingestion of hypochlorite solution | There is no information about the effects of prolonged ingestion of a hypochlorite solution in humans. In animals that drank a solution of hypochlorite in water for 2 years, no significant effects were observed. The amount of hypochlorite in the water the animals drank was much less than that in bleaching liquids for home use. |
| Skin exposure to hypochlorite solution | Spilling a hypochlorite solution on the skin may cause irritation. The severity of the effects depends on the concentration of sodium hypochlorite in the bleach. |
How can chlorine affect children?

This section discusses possible health effects in humans caused by exposures from conception to maturity (18 years of age).
| Similar effects in children and adults but children may be more sensitive | Brief exposures (minutes) to high concentrations of chlorine affect children and adults similarly (e.g., irritation of mucous membranes and respiratory tract). It is not known what effects could occur in children with prolonged exposure (weeks or longer) to low levels of chlorine, but this type of exposure occurs only in workers and is not applicable to children. It is also not known what effects could occur in children exposed to prolonged exposure to low levels of a hypochlorite solution. |
|---|---|
| Birth defects | It is not known whether exposure to chlorine gas during pregnancy can harm the fetus because there are no studies of pregnant women or animals exposed to chlorine gas. A study in rats exposed to a hypochlorite solution during pregnancy found no evidence of birth defects. birth or other developmental alterations in offspring. The amount of hypochlorite the rats consumed was much higher than what people normally consume through drinking water. |
Chlorine gas uses

What do we use sodium hypochlorite for?
Chlorine gas is used for manufacturing and disinfecting water
Chlorine is a very important industrial chemical used in the manufacturing of thousands of products. It is also used to disinfect water, although chlorine is quickly transformed into other substances at the beginning of the process.
Chlorine gas to purify water

Chlorine gas for drinking water
Generally the concentrationn of sodium hypochlorite for water purification cannot exceed 10%, and the amount of the product must be between 0.5 and 1 mg/l.
It should be noted that the sodium hypochlorite used in this procedure is not commercial chlorine, since the latter contains other chemicals that can be harmful to human health.
Sodium hypochlorite wastewater uses

Additionally, it is worth mentioning which is also used to treat wastewater and industrial water. This is because it eliminates unpleasant odors and prevents the spread of bacteria and sludge.
Chlorine gas for pools

To obtain all the details of pool chlorine, access our page dedicated to Secrets of pool chlorine disinfection:
How is chlorine gas made?

Manufacturing sodium hypochlorite
Process to make sodium hypochlorite
The first electrolytic process for the production of chlorine was patented in 1851 by Charles Watt in Great Britain. In 1868, Henry Deacon produced chlorine from hydrochloric acid and oxygen at 400ºC (750ºF), with copper chloride impregnated in pumice as a catalyst. Modern electrolytic cells can almost always be classified as belonging to the diaphragm and mercury type. Both produce caustic substances (NaOH or KOH), chlorine and hydrogen. The economic policy of the chlorine and alkali industry mainly includes balanced marketing or internal use of caustic and chlorine in the proportions in which they are obtained by the electrolytic cell process.
Obtaining Chlorine gas
Video how to make chlorine gas
This video shows the production of chlorine gas from the reaction between manganese dioxide and hydrochloric acid.
How to make homemade sodium hypochlorite
Procedure on how to make sodium hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite can be obtained by mixing chlorine with a sodium hydroxide solution in an aqueous medium, depending on the reaction.
Currently we obtain sodium hypochlorite through an electrolysis process in which elements such as salt, water and an electrolytic tank intervene. In this tank there is a positive pole and a negative pole, the positive pole gives off chlorine in a gaseous state that is recovered for the manufacture of hypochlorite and the negative pole gives off hydrogen that is eventually discarded.
How to make homemade bleach
Video how to make sodium hypochlorite
How to prepare sodium hypochlorite at 13
Sodium hypochlorite 13 how to dilute it
Next, in this video you will know the formula and how to know if your hypochlorite really is 13%,
Chlorine gas where to buy

Chlorine is the most used disinfectant chemical element in the pool

Chlorine is the most popular pool disinfectant
Chlorine (Cl) is one of the most common chemical elements used to eliminate microorganisms that can infect our water.
Chlorinated products are the substances most frequently used in chemical water treatment.
Different forms of Chlorine in water The objective of disinfection is to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms and guarantee the absence of any infectious germ (bacteria or virus) in the water. Chlorinated products are the substances most frequently used in the chemical treatment of water thanks to their safety and ease of controlling their levels.
As you may already know, chlorine is the most popular pool disinfectant, but there are many other disinfection methods currently in the industry that you can also use to keep your pool clean.
chlorine gas price
sodium hypochlorite buy
Chlorine gas buy
Next. Click the link and we will redirect you to our entry: Sodium hypochlorite where to buy all the different existing types
Automatic Floating Chlorine Dispenser for Pools and Spas

Automatic chlorine gas dispenser in swimming pools

Provide stable chlorine gas to the pool or spa to maintain adequate chlorine residuals in the pool.
Description automatic sodium hypochlorite dispenser for swimming pool
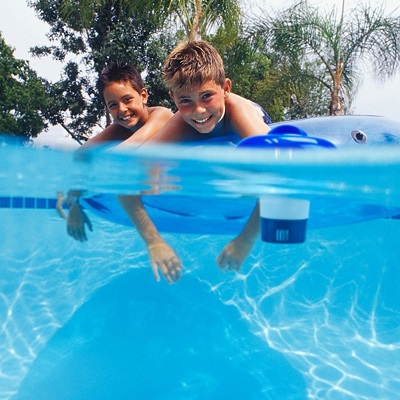

Pool chlorine dispenser product details
- Easy to use: simply open the lid, add the chlorine tablets slowly and place them in the pool after adjusting the output
- 【Adjustable Flow Connection】: Side connectors specially designed to control the release of chlorine. You can adjust the flow of the medicine to the actual situation of the pool
- Easy to Float: The chlorine tablet dispenser can easily float on the surface of the pool to distribute chlorine evenly without worrying about the chlorine content in your pool. Closing lid keeps chlorine tablets secure and offers a safer, more enjoyable pool experience
- High quality: made of high quality materials, safe, healthy and durable, can be reused
- Applicable scene: It can be used in your swimming pool, water park or spa and offers you a better water experience
How the floating chlorine dispenser works
floating chlorine dispenser use

Chlorine gas dosing system in swimming pools
Components required for a chlorine gas dispenser for swimming pools
The components that are part of this type of dosing system for swimming pools are shown.
Chlorine gas dispenser
Sodium hypochlorite dispenser buy
[amazon box= «B091T3S8YG, B0029424YU, B092M7QXZW » button_text=»Buy» ]
DULCO Chlorine Gas Dosing Systems®Vaq
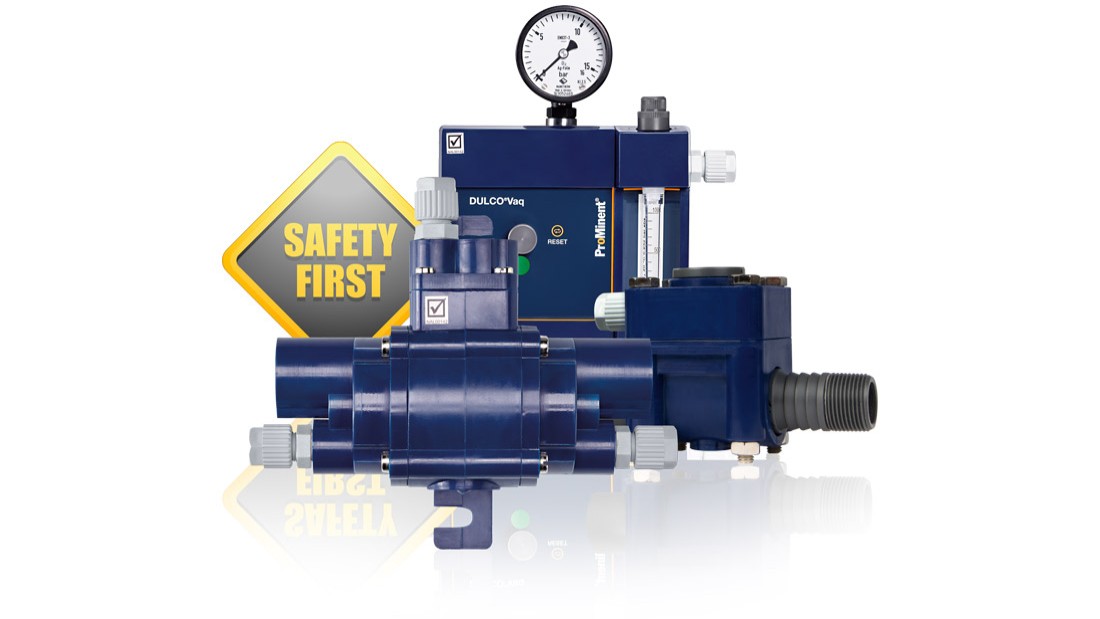

How the DULCO Sodium Hypochlorite System Works®Vaq
In the DULCO dosing system®Vaq chlorine gas is used with vacuum safely.
With the negative pressure generated in the injector, the vacuum dosing regulator mounted on the chlorine gas container opens, causing said chlorine gas to reach the water to be treated. Adjustment valves control the dosage amount and the flowmeter accurately indicates the flow rate of chlorine gas. Adding other components such as motorized regulating valves, injectors or vacuum selectors expands the possibilities of custom configuring the system.
DULCO components are used in industrial applications and in the treatment of large quantities of water.®ProMinent Vaq for large chlorine installations.
In this case, components such as evaporators, pressure reducing valves, pressure selectors, dosing devices and the corresponding room equipment are also used.
In specific project designs, ProMinent technicians ensure compliance with the latest safety regulations.
Features of the DULCO dosing system®Chlorine gas vaq

DULCO Chlorine Gas System Properties
Perfect safety for customer and user thanks to DULCO chlorine gas dosing systems®ProMinent Vaq.
- Chlorine gas dosing devices up to 200 kg/h
- Reliable chlorine evaporator in water bath
- Pressure and vacuum switch
- Emergency disconnection system
- Neutralizers/scrubbers
- Weighing systems in different configurations
- Power water pumps
- Safety equipment for the room
Application field DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
- Drinking water treatment
- wastewater treatment
- Cooling water treatment
- Swimming pool water treatment
Key Advantages DULCO Sodium Hypochlorite System®Vaq
Key Benefits of DULCO Sodium Hypochlorite System®Vaq
- Proven and sophisticated system
- Precise dosing even at high flow rates
- High degree of automation
- Robust design
- Complete product range for DIN19606 compliant installations
Buy chlorine gas dosing system
Buy DULCO sodium hypochlorite device®Vaq
Therefore, we provide you with the address to contact you.act with the distributor of DULCO dosing systems: DULCO Chlorine Gas Dosing Systems®Vaq
1st Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
DULCO vacuum regulator for chlorine gas®Vaq

Characteristics of DULCO vacuum regulator for chlorine gas®Vaq
Capacity: up to 200 kg/h
The DULCO vacuum regulator®Vaq CGVa doses chlorine gas economically and efficiently. The use of high-quality materials such as tantalum and silver guarantees maximum operating safety and reliability.
Key Advantages DULCO Chlorine Gas Vacuum Regulator®Vaq
- Maximum safety thanks to the integral vacuum system
- Maximum operating safety and reliability with high quality materials such as tantalum and silver
- Components and accessories adapted to each other
- Integrated safety ventilation
2nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
DULCO motorized regulating valve for chlorine gas®Vaq

Characteristics Motorized regulating valve for DULCO gaseous chlorine®Vaq
Capacity: 12 g/h to 15 kg/h
The DULCO motorized regulating valve®Vaq PM 3531 is responsible for electronically controlling the precise dosage of the chlorine gas flow. Linear regulation behavior is ensured by an externally controlled stepper motor.
Key Advantages DULCO Motorized Regulating Valve for Chlorine Gas®Vaq
- Linear regulation behavior for precise dosing
- Multitude of control and information functions
- Automatic and manual operation mode
- Calibratable
- Automatic safety shut-off
- Easy to control, for example with the DULCOMARIN® or the DACb Controller
3st Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
DULCO vacuum selector for chlorine gas®Vaq

Characteristics Vacuum selector for DULCO gas chlorine®Vaq
Capacity: 12 g/h to 120 kg/h
DULCO vacuum selectors®Vaq PM 400 and 440 switch to one of the two chlorine gas containers automatically and reliably. They thus facilitate an uninterrupted supply of chlorine gas even when one of the containers is empty.
Key Advantages DULCO Chlorine Gas Vacuum Selector®Vaq
- Automatic switching of chlorine gas sources
- Vacuum-only operating system without external auxiliary power
- Simple assembly and commissioning
4nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
DULCO gas chlorine injector®Vaq

DULCO gas chlorine injector properties®Vaq
Capacity: 12 g/h to 200 kg/h
DULCO series chlorine gas injectors®Vaq generate a stable vacuum even at high service pressures.
Virtues of the DULCO gas chlorine injector®Vaq
- Safe vacuum generation method
- Up to 40 bar back pressure
- Integrated return valve
- Various mounting possibilities
- Robust design
Notice: To choose the appropriate driving water pump, injector curves are available for all models.
5nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
DULCO automatic chlorine gas dosing device®Vaq

Peculiarities DULCO automatic chlorine gas dosing device®Vaq
Capacity: 12 g/h – 15 kg/h
The DULCO chlorine gas dosing device®Vaq type PM 3610 C ensures regulated automatic dosing of chlorine gas. The easy handling allows high safety and precision according to current technology standards, according to DIN standard.
Advantages DULCO automatic chlorine gas dosing device®Vaq
- Automatic chlorine gas dosing
- Plug and Play
- According to DIN 19606
- Board Mounted System
- Motorized regulating valve with different control options
- Functional cover
6nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
DULCO Automatic Emergency Disconnect System for Chlorine Gas®vaq

Singularities Automatic emergency shutdown system for chlorine gas
Automatic closing of chlorine gas valves in seconds.
Electrical emergency shutdown system for automatic shut-off of chlorine gas supply increases safety for personnel and equipment. The integrated control unit and interrupted power supply system reliably shuts off the chlorine gas valves in an emergency, even when a power failure occurs.
Pros Automatic emergency shutdown system for chlorine gas
- Close directly on the valve
- In an emergency, close any type of chlorine gas valve in a matter of seconds
- Electrical operation supported by an uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
- Adjustable torque moment for safe closing
- Option to upgrade existing chlorine gas installation systems
- Simple, tool-free assembly and disassembly when changing the container
7nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
Evaporator for chlorine gas DULCO®Vaq

Properties Evaporator for chlorine gas
Capacity range 50 – 200 kg/h
DULCO evaporator®Safe and reliable Vaq type PM3100C for liquid chlorine applications in large chlorine installations.
Prerogatives Evaporator for chlorine gas
- Safe handling of large quantities of chlorine
- Reliable water evaporator
- Easy installation
- Long service life thanks to cathodic corrosion protection
- High degree of automation
- Robust design
8nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
Neutralizer for chlorine gas DULCO®Vaq

Qualities Neutralizer for chlorine gas
Neutralization of 50 – 500 kg of chlorine gas
In case of alarm the DULCO neutralizer®Vaq absorbs chlorine gas that has escaped with the ambient air from the chlorine gas room and safely neutralizes it.
Merits Neutralizer for chlorine gas
- Neutralizes chlorine gas in the event of a leak
- It already neutralizes 99,9% in the water jet pump
- Safety and security of equipment
- Automatic operation
- Simple handling and maintenance
9nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
Pressure selector for DULCO gas chlorine®Vaq

Peculiarities Pressure selector for DULCO gas chlorine®Vaq
Capacity range up to 200 kg/h
DULCO pressure selector®Vaq type PM 481 for the uninterrupted supply of chlorine gas in high dosage volumes.
Benefits of the DULCO Pressure Selector for Chlorine Gas®Vaq
- Safe handling thanks to automatic operation and pressure control
- Continuous operation thanks to uninterrupted chlorine supply
- Easy handling
- Easy connection thanks to the supplied remote control
10nd Product DULCO sodium hypochlorite system®Vaq
DULCO chlorine gas dosing device®Vaq

Distinctions DULCO gas chlorine dosing device®Vaq
Capacity: 20 – 200 kg/h
SWEET®Vaq type PMR540 and 550C: powerful autonomous systems for precise gas dosing in water treatment.
Attributes DULCO gas chlorine dosing device®Vaq
- High stability thanks to GRP casing with reinforced frame
- Direct control of operation through vacuum indication
- More safety thanks to the vacuum return valve
- Precisely adjustable thanks to the built-in flowmeter
- High degree of automation thanks to the motorized regulating valve
Automatic dosing of chlorine tablets for swimming pools

To keep pool water clean and in optimal hygienic conditions, the correct dosage of chemical products is essential.
There are basically two types of sodium hypochlorite dispensers:
1st type of sodium hypochlorite dispensers: liquid dosing pumps
- (e.g. pHMinor liquid for regulating the pH value, liquid disinfectants such as sodium hypochlorite or Oxy-Active Liquid)
2nd model of sodium hypochlorite dispensers and tablet dispensers
- (e.g. Trichlorine Compacts, Bromine Tablets). By additionally incorporating measurement and regulation technologies such as Poolwatch or Controller equipment we can completely automate the addition of chemicals to the pool water.
Chlorine dispenser characteristics

Chlorine dispenser details
• Simple and safe operation.
• They adapt to any pool or spa.
• Adjustable according to the size of the pool.
• Easy in-line or by-pass installation.
• Minimal maintenance.
• They do not need electrical current.
• Constructed of material resistant to chlorine and bromine.
• Anticorrosives.
Principle of operation of a chlorinator/brominator
The tablet dispensing equipment allows the Compact Trichlorine and Bromine Tablet products to be applied continuously, achieving the correct disinfection of the water.
Its operation is very simple: The chlorinator/brominator is filled with the tablets to be dosed and the inlet valve is regulated until the desired concentration of chlorine or bromine in the water is achieved and maintained.
Operation Automatic pool chlorine dispenser

Recommendations for the sodium hypochlorite dispenser
Suggestions for the use of the sodium hypochlorite dispenser
• Before starting to use a tablet dispenser, read the Instruction Manual carefully.
• They only work with slowly dissolving chlorine and bromine tablets (Trichlorine and Bromine Tablet Compacts). Never use any other type of chemical product in the dispenser (never powder, granular or fast-dissolving products).
• Wintering: In cases of prolonged non-operation, always empty the dispenser and remove the load from inside.
• Attention when opening the dispenser: follow the instructions exactly. Disconnect the pump. Protect your hands and eyes and do not breathe the gases from the dispenser!
• To find the ideal flow rate we recommend measuring the residual value of free chlorine or bromine in the water with the Test Strips with a Comparator (DPD method) or a Pooltester (DPD method)
Aid in case of chlorine gas spill

Assistance in case of chlorine gas leak
Chlorine gas leak relief
In extreme cases it can generate serious blisters on the skin, cause pulmonary edema and although the probability is very low, there are cases of death. If these serious cases occur, you should immediately go to a medical center for a corresponding check-up and treatment.
What to do when you inhale chlorine gas
In these situations, the contaminated person should be immediately removed from the exposure area and placed in a position in which their head and shoulders are kept elevated. If you notice difficulty breathing, artificial respiration should be provided, if possible, give oxygen immediately or as soon as possible.
Call an ambulance or go to a medical center right away.
What to do when sodium hypochlorite comes into contact with the eyes
Eyes should be washed with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, after a few minutes repeat the procedure again. Call an ambulance as soon as possible or go to the nearest medical center.
When there is contact of chlorine gas with the skin
The contaminated person should remove their clothing immediately and go to the showers to wash their entire body with plenty of water. Use soap a few minutes after playing with water.
Evacuate in case of leak
When a leak is suspected, the personnel operating in the exposure area must be evacuated and the corresponding measures taken to detect and seal the leak. Maintaining regular checks are the best way to avoid accidents. Implement all security protocols and train your staff to ensure their integrity.
Reproduction of an alleged chlorine gas leak
Video simulation of chlorine gas leak in a water treatment plant
How to neutralize chlorine gas

Chlorine gas neutralization
How to neutralize chlorine gas
In the event that chlorine gas escapes from storage tanks, drums, chlorine gas bottles or chlorine dosing equipment, the chlorine leak warning equipment alarm is activated and the chlorine leak warning equipment is immediately and automatically deactivated. GAS-CHLORINE cleaning from Likusta. The exhaust gas is carried away by a chemical-resistant plastic fan of the Likusta counterflow material scrubber and neutralized countercurrent with a cleaning liquid, usually caustic soda. The reactive heat expelled during the chemical washing process is absorbed by the cleaning fluid.
How to contain a chlorine gas leak?

How to understand a chlorine gas leak
One of the main tools that you can count on in a chlorine gas system is a chlorine gas neutralization tower or also called SCRUBBER, this system allows to address the emergency of a leak caused by ton cylinders or 68kg cylinders, which through an extractor system absorbs the chlorine gas, passing it through a dry or moist neutralizing medium, which generates a reaction that allows it to be emitted. the gas in quantities that are not toxic to the environment, and with byproducts such as hypochlorite and salts, which are easily available.
What is a chlorine gas wash or Scrubber?
Scrubber systems are a diverse group of air pollution control devices that can be used to remove some particles and/or exhaust gases from industry streams. Traditionally, the term "scrubbing" has referred to pollution control devices that use liquid to wash unwanted contaminants from a gas stream. Recently, the term is also used to describe systems that inject a dry reagent or slurry into a dirty exhaust stream to "wash" the acid gases. Purifiers are one of the primary elements that control gas emissions, especially acid gases. Scrubbers can also be used for heat recovery from hot gases by condensation of flue gases.
Chlorine gas washing tower operation

For gas decontamination to be complete, the system must be designed so that the transfer of matter from the gas phase to the liquid phase is maximum:
- The contaminant and the liquid must be compatible, that is, the solubility of the first in the second must be sufficiently high.
- The contact surface must be large enough so that there is no limitation on the transfer of the contaminant to the absorbent liquid.
- The contact of the contaminants present in the gas flow with the liquid depends on the type of absorption column.
Passing through the washing tower, the contaminated air is washed at low speed inside a large contact surface.
It is very important to use the appropriate type of absorbent during this process to ensure greater gas/liquid contact. Once purified, the air moves to the next stage or is released directly into the atmosphere.
1. Air passes through a compact column on a large contact surface.
2. Washing solution is continuously sprayed by centrifugal pump through nozzles and replaced automatically as required by ARRS.
3. Automatic water filling system (AWRS) ensures that the working level of the liquid is maintained.
4. The base of the column is a wash solution tank.
Scrubber gas scrubbers
Video description Scrubber to neutralize pool chlorine gas
These washing and/or neutralization systems can be complemented with instrumentation that results in the safety of the system.
a, the type and amount of instrumentation will depend on the installation conditions, and the degree of automation required, for example equipment can be installed that automatically closes the cylinder valves, when they receive a signal emitted by the installed leak detectors in the chlorine rooms, thus increasing the safety factors of the areas at risk.
The Scrubber or neutralization towers, which are also known as washing tower They can be handled with a wet neutralizer or a dry neutralizer. The advantages of using a dry tower are the ease in disposing of the product once an emergency occurs and it has a lower risk for operating personnel, given that the wet tower is You must have caustic soda between 25% and 30%, which can generate a high risk, as it is a chemical.
Washing solution to neutralize chlorine gas

The equipment can be designed with one, two or the following three washing stages. The 3SCR is a three-stage scrubbing removal system for high contaminant streams.
- Acid: To reduce alkaline contaminants, mainly ammonia. The solutions commonly used are sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid.
- Basic: For the reduction of acidic contaminants, such as sulfuric, hydrochloric, nitric, hydrofluoric or hydrobromic acid. Mainly sodium hydroxide is used.
- Oxidizer: For odor elimination and disinfection. Sodium hypochlorite or peroxides are mainly used.
or so aggressive; However, the initial investment costs for a dry tower are much higher.
The importance of installing a system of this style to neutralize chlorine gas
, allows you to ensure a protected area, when there are nearby populations of people who may be affected by an emergency with this chemical, taking into account all the safety, control, maintenance and good use of the systems recommendations, will ensure proper use of all the elements, and will allow, to give optimal treatment to the water or process in which it is used.
Chlorine gas as a chemical weapon
Chlorine gas first world war

Chemical weapons in World War I
The First World War is synonymous with trenches and also with chemical weapons. They were used on a large scale, after their introduction into the conflict by German forces in 1915.
What country used chlorine in World War I?
The first to use it in combat were the Germans. On December 19, 1915, 4.000 cylinders loaded with 75% chlorine and 25% phosgene were used against the British in Wieltje, Belgium, causing more than a thousand casualties, 120 of them fatal.
chlorine gas as a weapon
In January 1915, Fritz Haber received authorization to study chlorine attacks. His team, in collaboration with the three large German chemical companies of the time (BASF, Hoechst and Bayer) and other renowned scientists, such as Otto Hahn, James Franck and Gustav Hertz, set to work to design chemical weapons.
Chlorine gas as a chemical suffocating weapon
The first was chlorine gas which acts as a suffocating agent.
It was designed more as an incapacitating weapon than a deadly weapon, although it did not fail to produce numerous deaths.
The Germans had used tear gas in 1914, but chlorine was first fired at Ypres on April 16, 1915.
During the first German combined chlorine/phosgene attack, launched against British troops at Nieltje, near Ypres, Belgium, on December 19, 1915, 88 tons of gas packaged in cylinders were released, causing 1.069 casualties and 120 deaths. .
Despite its simplicity, its effect was enormous because it was a completely new weapon.
Chlorine gas Syrian war

Chlorine gas conflict Syrian war
Although the Syrian conflict has been the most documented in history, with evidence of the brutal use of chemical weapons and cluster bombs against civilians, this arsenal of documentation has not led the international community to take action against these rights violations. humans
Subsequently, you can find more information on this topic in the following article: YouTube and Twitter, the speakers of the Syrian war that the UN ignored
Indiscriminate bombing of civilians with chlorine gas in the Syrian war
But now, the doctors told him that the latest bombs released toxic clouds of chlorine gas.
Chlorine gas had rarely been used as a weapon since World War I and its use in Syria represented a serious violation of international standards.
Video chlorine gas as a chemical weapon
In this video I will explain a small synthesis of chlorine gas used in war conflicts, everything I teach you is for scientific use and without the purpose of harming others.
Mustard gas and chlorine: chemical weapon

Mustard gas was the main protagonist of the first chemical war in history
The most infamous and effective gas of World War I was mustard gas,
a vesicant introduced by the Germans in July 1917 before the Third Battle of Ypres. Known to the British as HS (o Hun Stuff), mustard gas was not intended to be a lethal agent (although it was in high doses), but rather was designed to harass and incapacitate the enemy and contaminate the battlefield. It was fired inside artillery shells, and was heavier than air. It settled on the ground as a sherry-like liquid, and slowly evaporated without the need for sunlight.
Effects of mustard gas on the human body
Chlorine phosgene gas

Toxic chlorine and carbon oxide gas
The chlorogene gas was more toxic than chlorine and its symptoms took several hours to manifest.
Phosgene chlorine gas: It was the most used agent during the conflagration.
More toxic than chlorine, it had a latency of several hours from the time the victim was exposed until the first symptoms appeared. The combatants were not aware that they were being poisoned.
The first to use chlorine phosgene gas in combat were the Germans.
On December 19, 1915, 4.000 cylinders loaded with 75% chlorine and 25% phosgene They were used against the British at Wieltje, Belgium, causing more than a thousand casualties, 120 of them fatal. It took six months for the Allies to respond using canisters filled with a 50/XNUMX mixture of chlorine and phosgene, called “white star.”
What is chlorophosgene gas
Phosgene poisoning
Chlorine gas chemical weapons in World War I
Sodium hypochlorite chemical weapons in World War I
News theft of the chlorine gas cylinder in Chihuahua

chihuahua chlorine gas
Where did the theft of the chlorine gas cylinder occur in Chihuahua?
According to the data provided by the Municipal Water and Sanitation Board (JMAS) Chihuahua, the event occurred on the afternoon of this Tuesday, July 27, when unknown persons vandalized the well located in the Punta Oriente neighborhood, in the extension of R. Almada and Paseos del Sol avenue, and they robbed the chlorine gas cylinder.
What states were alerted?
Due to theft, Civil Protection announced that the states Chihuahua, Coahuila, Durango, Sinaloa y Sonora They received an alert to be alert to any anomaly related to this case.
Source of information: https://www.unotv.com/nacional/chihuahua-roban-cilindro-de-gas-cloro-hay-alerta-en-cinco-estados/
Theft of the chlorine gas cylinder in Chihuahua in June 2021
Stolen chlorine gas tank recovered in Chihuahua
At the end of July 2021 in Chihuahua, an investigation by the Investigation Unit for the crime of Theft of the Central Zone District Prosecutor's Office allowed the recovery of a chlorine gas tank, recently stolen from the facilities of the Municipal Board of Water and Sanitation (JMAS).
Finally, the chlorine gas tank was located in a materials purchase and sale business located on Punta Armera Street in the Punta Oriente neighborhood, proceeding to secure it with the help of specialized personnel from the JMAS for its management.
