Table of contents of the page
En Ok Pool Reform within pool water maintenance guide We want to introduce you to the following article: How to measure pool water alkalinity.
pool alkalinity what is it

Pool Alkalinity: fundamental parameter in the disinfection of pool water
First of all, highlight that One of the basic parameters to control when carrying out maintenance is the alkalinity along with the pH of the pool.
How to carry out a correct treatment of the pool water chemistry
Alkalinity is a measure of the buffering properties of water.
It is measured in milligrams of calcium carbonate per liter (mg/L) and is usually in a range of 80-120 mg/L.
Alkalinity has a definite impact on pH because it acts as a reservoir for hydrogen ions that can neutralize acids and make a change in pH less likely.
Therefore, an alkalinity value of 80-120 mg/L ensures that the pH will be somewhat stable even if the water chemistry changes.
Additionally, alkalinity plays a role in the corrosion of metals, acting as a moisture barrier that protects metal surfaces from damage.
Therefore, an adequate alkalinity value is important for residential and commercial water users alike.
What is pool alkalinity
To begin, explain that the alkalinity is ability of water to neutralize acids, a measure of all alkaline substances dissolved in water (carbonates, bicarbonates and hydroxides), although borates, silicates, nitrates and phosphates may also be present.
Alkalinity acts as regulatory effect of pH changes.
So, if you do not preside with the appropriate values, you will not be able to have well-disinfected and transparent water in your pool.
Recommended pool alkalinity level
Pool alkalinity recommended is between 125-150 ppm.
Reminder: in some cases, the water may have a correct pH, but the alkalinity may be low or high.
How pool water pH and alkalinity are linked

What is pool pH
Natural increase in pH: loss of carbon dioxide
The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm of the value of the average concentration of hydrogen ions.
- Since H ions can dissociate into H2O and H2CO3, the pH can be modified in two ways: by adding or removing H2O or by adding or removing H2CO3. When carbon dioxide is lost from a pool through evaporation, the pH increases.
- This is because H2CO3 has a much higher acidity than H2O; In terms of acid equivalence, the K w of H2CO3 is 3400 compared to the K w of H 2O of 25.
- In terms of Henry's law, the K a for CO2 is 3,18. As the pH increases, the concentration of H ions increases, and the excess protons will eventually “ionize” and become H2O and H2CO3.
Therefore, in an acidic pool, the rate of change in pH is ultimately limited by the rate of reaction between H2CO3 and H2O.
- ; This speed depends on the temperature, as well as the presence of inhibitors such as calcium sulfate or bicarbonate.
- Therefore, it is important to control pH in conjunction with the rest of the pool chemistry, rather than using traditional pH control methods with fixed target values.

This diagram shows how carbon dioxide (CO2) is removed from water when it is aerated.
- When water is aerated, the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water begins to dissolve naturally in the water.
- Excess carbon dioxide rises to the top of the pool, where it can be captured and vented into the atmosphere.
The colder the pool, the faster the CO2 will leave the water naturally.
- In hot, sunny climates with a lot of evaporation, it may even be necessary to aerate the water several times a day to keep carbon dioxide levels within the desired range.
Diagram of the CO equilibrium process2,

CO2 naturally tends to seek equilibrium between the surface of the water and the ambient air.
Therefore, CO2 is released until it is in relative equilibrium with the air above the pool. This phenomenon is known as Henry's law.
CO2 naturally tends to seek equilibrium between the surface of the water and the ambient air.
Therefore, CO2 is released until it is in relative equilibrium with the air above the pool. This phenomenon is known as Henry's law.
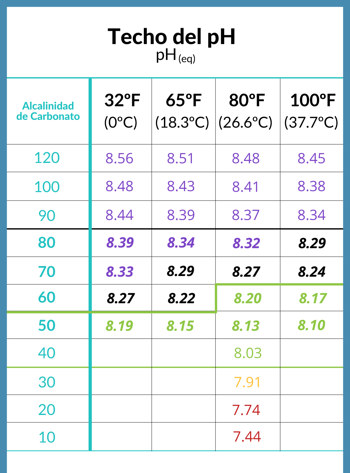
Connection between pool water pH level ceiling and alkalinity
High ph pool water and correlation with alkalinity
- In aquatic systems, pH has a large impact on water chemistry.
- pH controls the concentration of different ions, and changes in pH can influence the types and number of species that are present.
- For example, a pH of 7 is ideal for maintaining ecosystem function, but a pH of 8 may be too low for some organisms and too high for other species.
When the CO2 in the water reaches equilibrium with the air above the water surface, the pH is said to have reached its ceiling, and that ceiling is determined by the level of carbonate alkalinity in the water.
- The pH ceiling, or the pH value that is ideal for the water as a whole, is determined by the carbonate alkalinity of the water.
- Different roofs in different circumstances can be seen in the following table provided by chemist Richard Falk.
How pool alkalinity and water pH are different
Difference Between Pool Alkalinity and Water pH Level
Have you ever wondered what the difference is between pH and alkalinity?
When the alkalinity level is considered to be high
On the one hand, when the concentration of calcium carbonate is Above 175 ppm, we speak of high alkalinity.
High alkalinity affects
Next, we mention some of the effects that are produced when alkalinity is high.
- Significant increase in pH.
- Non-transparent, apparently cloudy water.
- Irritation of the eyes, ears, nose and throat.
- Formation of incrustations on walls and accessories.
- Acceleration of wear and tear of pool materials.
- Loss of effectiveness of the pool disinfectant.
What causes high alkalinity?
A rise in alkalinity can be due to various factors. They stand out among them:
- Evaporation of water due to changes in water volume due to the action of the sun and wind can cause an increase in alkalinity.
- Alkalinity tends to increase through the use of the pool, due to the effect of sun creams, sweat and waste...
- Sometimes when we fill the water, if it has been in contact with carbonate rocks it can result in a high alkalinity pool.
- Misuse of chemicals.
- Malfunctions in the pool filter system.
How to lower pool alkalinity
How to Reduce Pool Alkalinity
- First, we must turn off the pool pump and wait approximately one hour.
- Next, it is necessary to add (according to convenience) the necessary amount of pH reducer and distribute it to transform it into bicarbonate into carbon dioxide. NOTE: To reduce pool Alkalinity by 10 ppm, you need to distribute about 30 mL for each cubic meter of pool water (whether in liquid or solid format).
- Then, after an hour, we turn the pump on again.
- After about 24 hours, we will measure the alkalinity levels again.
- On the other hand, if we observe that the pool water alkalinity levels have not decreased in 2 or 3 days, we will repeat the process (sometimes it can be an expensive process).
- In addition, we must check the pH levels at all times, as they can drop.
[amazon box= «B00PQLLPD4 » button_text=»Buy» ]
When the alkalinity level is considered to be low
In this case, when the concentration of calcium carbonate is Below 125 ppm, we speak of low alkalinity.
Consequences of low alkalinity
Among the effects produced by the drop in alkalinity in water we can find:
- Generally, the pH of our pool will be low. Furthermore, it will be difficult to control and stabilize it.
- Due to these circumstances, we will consume a lot of disinfectant since it does not have the same efficiency.
- Overstress of filtering systems.
- The water in our pool will look green.
- It leads to corrosion and stains on the metal parts and accessories of the pool.
- It also causes irritation of the eyes, nose, throat and skin.
- Finally, if low alkalinity is combined with a low pH, algae will form in the water, making it look green.
What causes low alkalinity?
An unexpected drop in the alkalinity level in pool water may be due to the following factors:
- Inappropriate products when performing pool maintenance (avoid using tablets with multiple functions, the water becomes acidic).
- One factor may be that the pool's filtration equipment is not working properly.
- If there are strong climatic temperature alterations.
increase pool alkalinity
How to increase pool alkalinity

How to Increase Pool Alkalinity
Raise alkalinity
increase pool alkalinity: it is the most common case
This is the most common case, since the alkalinity of tap water is usually very low (in several areas of Spain it is as low as 10 or 20 ppm). And also because the most common correction of the pH regulator is to reduce the pH that has been rising with the chlorine, and to reduce the pH we dose an acid, which also reduces the alkalinity (although to a much lesser extent than the pH).
Increasing the alkalinity of your pool water can be one of the first steps in restoring balance.
- When your water has a low pH, it can affect the pH of your pool and create several problems, including cloudy water and lack of clarity. To help increase the alkalinity of your water, you can use baking soda powder or baking soda crystals. Be sure to only use the recommended amount for your pool or spa, as too much can have an adverse effect on the pH of the water. When you start to see an improvement in water clarity, you will need to continue monitoring alkalinity levels to make sure they stay where they need to be.
increase pool alkalinity bicarbonate
To increase alkalinity it is best to use baking soda.
Increasing the alkalinity of your pool water can be one of the first steps in restoring balance. When your water has a low pH, it can affect the pH of your pool and create several problems, including cloudy water and lack of clarity. To help increase the alkalinity of your water, you can use baking soda powder or baking soda crystals. Be sure to only use the recommended amount for your pool or spa, as too much can have an adverse effect on the pH of the water. When you start to see an improvement in water clarity, you will need to continue monitoring alkalinity levels to make sure they stay where they need to be.
Baking soda is a white powder, easy to dissolve in water and handle, it is not particularly toxic and does not damage the skin if touched, so it will be easy to dose and pour into the pool. Furthermore, sodium bicarbonate does not contribute to the aging or toxicity of water (in another article we will talk about what is meant by aged water...).
You can also use sodium carbonate
, and caustic soda, but we do not recommend it, since they interfere much more with the pH, and what it is about is trying to raise the alkalinity with the least possible effect on the pH (so that the whole process is simpler) .
To give you an idea, to increase alkalinity by 10 ppm, the effect on pH depending on the substance used is:
Baking soda: the pH would increase by 0,017
Sodium carbonate: the pH would increase by 0,32
Caustic soda: the pH would increase by 0,6
This is an example of the pH-increasing effect that alkalinity can have on the acidity of water. To give you an idea, to increase alkalinity by 10 ppm, the effect on pH depending on the substance used is:
Baking soda: the pH would increase by 0,017
Sodium carbonate: the pH would increase by 0,32
Caustic soda: the pH would increase by 0,6
This is an example of the pH-increasing effect that alkalinity can have on the acidity of water. To give you an idea, to increase alkalinity by 10 ppm, the effect on pH depending on the substance used is:
How much baking soda do I need?
The rule is that you need 17,3 grams of baking soda to raise the alkalinity by 10 ppm for every m3 of your pool.
Or what is the same:
Amount in grams = (Desired Alkalinity – Current Alkalinity) x (m3 pool) x 1,73
NOTE: Remember that these calculations are estimates and may vary from one pool to another.
Let's give an example for a 50 m3 pool, and the current alkalinity level of 30 ppm. In this case we will want to reach 100 ppm, so we need:
(100 – 30) x 50 m3 x 1,73 = 6055 grams of baking soda (6 kg, to round up).
How should I manage it?
The ideal is to go little by little. There are theoretical formulas for the maximum amount of chemicals you should put into the pool each day. In this ideal world, the maximum amount of baking soda in a 50 m3 pool would be 360 grams per day. But we know that many times it is not feasible, because there is no time. With the water we have in many places, it would take almost a month to correct the alkalinity. Or in the case of eliminating algae, we cannot take that long.
Therefore, try to go little by little, as you have time, since the chemistry of water appreciates that the changes are as gradual as possible.
To administer baking soda, dilute in water, turn on filtration, and administer throughout the pool, as with almost all chemicals. And leave the filtration on for about 4-6 hours.
It is recommended to deactivate the pH regulator while doing this process. When sodium bicarbonate is administered, the pH will rise, but it will be momentary, then it will stabilize.
We have not mentioned pH in this entire process. When alkalinity needs to be increased, we will focus on establishing its ideal level, and then we will measure and adjust the pH next.
If the pH was high before raising the alkalinity, the sodium bicarbonate will not raise it substantially, this high pH after the alkalinity must be corrected.
And if the pH was low, it will rise a little as the alkalinity increases, but it is better to wait until the alkalinity is at an adequate level before adjusting it. Also remember that with low alkalinity, the pH is not protected, and high or low pH levels may be due to this lack of protection. That is why you have to wait until you have an alkalinity between 80 and 100 and then measure and adjust the pH.
Reduce alkalinity
It is not common to have to reduce alkalinity. Because the supply water usually has a low level, and because the normal thing is that the pH regulator always has to reduce the pH (and when dosing acid there is also a reduction in alkalinity).
But there are cases, such as in some groundwater, that the supply comes with a high pH and alkalinity. Or it also happens that chemicals have been added indiscriminately to the water, producing strong imbalances, one of them being high alkalinity.
To reduce alkalinity the method is different if the pH is high or low:
Reduce alkalinity with high pH
You should not try to lower the pH since it will be very very difficult. A high alkalinity has a high power to neutralize acids (it is the definition of alkalinity), and any acid that we inject will affect the pH very little.
And in these cases, the technique consists of injecting etching (also called hydrochloric acid or salfuman or muriatic acid) as far as possible into the bottom of the pool (with a tube, for example). We must use hydrochloric acid as concentrated as possible, ideally at 30%.
When we inject the acid, we have to turn off the purifier, and it does not turn on until the next day.
The amount of hydrochloric acid in cc and 30% that we need is:
1,55 x (m3 of pool) x (current alkalinity reading – desired alkalinity level)
With our example of the 50 m3 pool, and assuming that we start from an alkalinity of 180 ppm, to reach an alkalinity of 100 ppm we need:
1,55 x 50 x (180 – 100) = 6200 cc = 6,2 liters of 30% etching
We should not try to lower more than 40-50 ppm of alkalinity each day. If necessary, divide it into several sessions.
After 24 hours we measure the level of alkalinity and pH, and we can find 3 scenarios:
- Alkalinity between 80 and 120, and pH in range as well (approximately less than 7,5 for pools with chlorine, and 7,8 for pools with bromine): in this case we are ok, we are done, it was easy.
- Alkalinity still above 120, and pH greater than or equal to 7,2. We can repeat the procedure of injecting etching, but aiming to lower the alkalinity by 10 ppm. This is because the pH is almost at the limit, and if we go too far it will drop to a level from which we will not be able to raise it later.
In fact, if in any of the sessions the pH drops below 7,0 we should not continue, and we will have to apply the method explained below of reducing alkalinity with low pH. - Alkalinity still high, but pH below 7,0 – 7,2: we should not continue, we must apply the technique of reducing alkalinity with low pH.
Reduce alkalinity with low pH
When the pH is low and the alkalinity is high it is the worst scenario, since that is when it is most difficult to regain balance. If we apply acid, the pH will drop further, and then bases will have to be supplied to balance it, but they will cause the alkalinity to rise again, and we enter a loop. Remember that pH and alkalinity are almost always modified in the same direction, and that is why driving them in the opposite direction is not obvious.
Since we cannot raise the pH with pH increasers (because the alkalinity will increase more), then we must use a method known as aeration, by which the water is subjected to a physical procedure by "injecting" air so that it loses its dissolved gases. specifically carbon dioxide (CO2 ). Without going into much chemical analysis, say that by dissolving CO2 In water, its pH decreases, and if we manage to remove it from the water, we will increase it.
You read correctly, by aerating the water well we manage to remove CO2 and increasing its pH, without adding any chemicals, is a physical process.
There are several ways to aerate water, whatever you can think of. You can orient the impellers to create a little whirlwind, but the effect is small. You could splash around all night…. But the most useful thing is that you make a small "fountain": with PVC pipe and a pair of elbows you make a kind of giraffe; You connect one end to an impeller, and at the other you put a PVC plug in which you make small holes, as if it were a shower head. The bottom elbow can be 45 degrees so that they "plug" the water more directly into the pool.
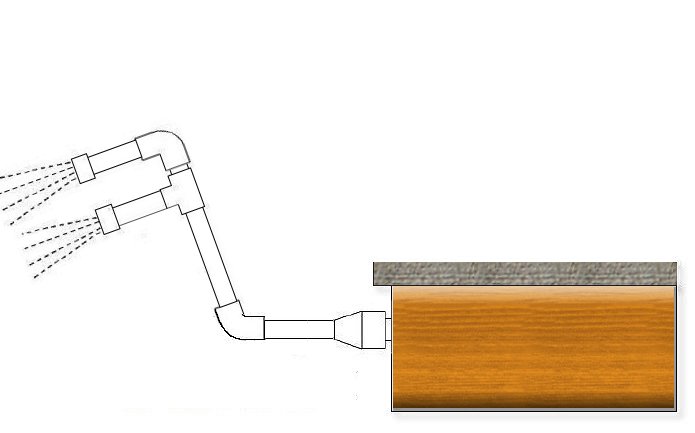
You turn on the filtration, and if you can cover the other impellers so that the pressure is higher, the better. It takes hours of operation, depending on the size of the pool and the pH level, but you will have to have it running no less than 6-8 hours. And you will see that the pH will have risen slightly.
The elbows and pipe are easy to get, it may be more difficult how to attach it to the impeller. If your pool impellers are the typical white ABS ones with a screw cap, you can join a 32 mm PVC pipe with the following piece:

Once we manage to raise the pH to 7,2, we inject the hydrochloric acid again to lower the alkalinity. The higher we have taken the pH, the better, since we will be able to correct a greater amount of alkalinity. If we can raise it to 7,6, even better. Remember that there is no need to make an alkalinity correction that would lower the pH below 7,0 – 7,2
IMPORTANT NOTE: Yes, yes, as you just discovered, waterfalls, waterfalls, etc. in swimming pools they are not «harmless“... have a direct effect on raising pH, so its use (or abuse) may be contraindicated depending on the conditions…
Buy Pool alkalinity increaser
Pool alkalinity increaser price
[amazon box= «B071458D86, B07CLBJZ8J , B071458D86, B08TC3DZZD» button_text=»Buy» ]
Pool water alakalinity meter

Measurement to measure alkalinity: analytical strips.
To measure the total alkalinity of the water, you can use simple analytical strips (measurement of 4 or 7 parameters) that will allow you to find out its value in an easy and quick way. Likewise, you can also measure with a wide variety of digital meters or even photometers.
Buy products to measure pool alkalinity
Alkalinity is usually measured with a pH meter, which detects pH changes in the liquid being tested.
Alkalinity test for swimming pools
HOMTIKY WATER STRIPS 6 IN1 50PCS
The appearance of this product is a thin strip, with one end of the sensing blocks arranged according to the scientific distance and the other end for manual position. One test strip of this product can simultaneously detect six important sample elements. Within 30 seconds, total hardness, free residual chlorine, total chlorine, cyanuric acid, total alkali and pH of sample water can be detected.
How to use the pool alkalinity test
Easy to use alkalinity test for swimming pools
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
| Pool pH Test StripsIt is designed for the measurement of total chlorine, free chlorine, pH, total alkalinity, cyanuric acid and total hardness. | Open the BottleEach 10 unique pieces are in an aluminum outer packaging, protected from moisture. | Take out the test stripTake out the test strip and close the bottle cap tightly after use. |
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
| Immerse it in waterImmerse the colored part of the test strip in water and take it out after 2 seconds. | Wait 30 seconds Extend the test strip and wait 30 seconds. | View Results Compare the test strip to the color card on the bottle and complete the reading within 30 seconds for accurate results |
Description of detection elements
Total hardness
Total hardness refers to the amount of calcium and magnesium in the water. The total hardness of pool and spa water should be between 250 and 500 mg/L.
Free residual chlorine, total chlorine
Chlorine is the most common disinfectant in pool and spa water, and its primary purpose is to disinfect and oxidize contaminants in the water, thus providing protection to swimmers. Chlorine that has active wells and is capable of oxidizing contaminants in water is called free residual chlorine. Chlorine that has exhausted its disinfecting power by reacting with contaminants is called combined chlorine. Total chlorine is the sum of residual free chlorine and bound chlorine. The residual free residual chlorine in the swimming pool should be between 0,3 and 1 mg/L, and the recommended free residual chlorine in thermal water should be between 3 and 5 mg/L.
cyanuric acid
Cyanuric acid, also known as a "stabilizer" or "conditioner," makes chlorine more stable when exposed to the sun's ultraviolet rays. Two chlorine compounds (dioxy and trioxy) already contain some cyanuric acid. Continued use of any of these disinfectants may increase the level of cyanuric acid. The cyanuric acid content must be less than or equal to 50 mg/L.
NOTES:
To obtain cyanuric acid test results, the pH must be between 7.0-8.4 and the total alkalinity must be less than or equal to 240 mg/L.
Total alkali
Total alkalinity is a measure of the amount of alkaline substances (mainly bicarbonates and carbonates) in water. If sodium chloride, sodium trichloride, or ointment is used as a disinfectant, the total alkalinity should be in the range of 100 to 120 mg/L. If calcium, sodium, or lithium hypooxide is used as a disinfectant, the total alkalinity level should be in the range of 80 to 100 mg/L.
PH
pH refers to the strength of acidic or alkaline substances in water. pH 7,0 is neutral and the pH range of pool and spa water should be between 7,0 and 7,8.

Notes:
1. Do not put wet fingers in the bottle.
2. Do not touch or contaminate the test strip test block with your hands.
3. Tighten the cap after each test strip removal.
4. Compare the color of the test strip in good light to obtain a reading.
5. Store in cool, dry and dark conditions.
6. It is recommended to consume within 90 days of opening.
Precautions for the use of chemical reagents:
1. Do not add chemical reagents when the pool is in use.
2. When adding acid, acid should be added to water, but water should not be added to acid.
3. All chemical reagents should be used carefully and strictly follow the instructions for use.
Buy pool alkalinity test
Price of test strips pool water alkalinity meter
Buy item to measure pool alkalinity


